Cucumber Processing Plant: Key Steps And Equipment
Cucumbers, beloved for their refreshing crunch, don't magically appear in your pickle jar or salad bag. A sophisticated dance of technology and food science happens within a cucumber processing plant. Let’s peek behind the scenes at the key steps and essential equipment that transform raw cucumbers into the products we enjoy.
1. Receiving & Initial Inspection:
Step: Truckloads of cucumbers arrive directly from farms. The first critical step is quality control.
Equipment: Dumping stations (often using water flumes to cushion the fall), conveyor belts, and inspection belts. Trained staff or basic optical sorters remove grossly damaged, oversized, undersized, or off-color cucumbers. Samples are taken for testing (pesticide residues, etc.).
2. Washing & Cooling:
Step: Removing field heat quickly is vital to preserve crispness and slow decay. Dirt, debris, and surface microbes must be thoroughly washed off.
Equipment:
Hydrocoolers/Flume Tanks: Cucumbers are submerged in chilled, often chlorinated (for sanitation), water. Agitation (water jets, bubbles, paddles) ensures thorough cleaning. This rapidly cools them.
Brush Washers: Rotating brushes scrub the cucumber skin gently but effectively as they pass through on conveyors, often combined with water sprays.
3. Grading & Sorting:
Step: Cucumbers are precisely sorted by size, shape, color, and quality to meet specific product requirements (e.g., whole pickles vs. spears vs. relish).
Equipment:
Size Graders: Often roller graders or belt-and-rod sorters. Cucumbers roll over gaps of increasing width; smaller ones fall through first onto different conveyors.
Electronic/Optical Sorters: Advanced systems using cameras and lasers detect color defects, surface blemishes, and even internal flaws, triggering air jets to reject substandard cukes.
4. Cutting & Sizing (If required):
Step: For products like spears, chips, slices, or relish, cucumbers need precise cutting.
Equipment:
Automatic Slicers/Dicers: High-speed rotary blades or hydraulic guillotine-style cutters produce consistent slices, spears, or chunks.
Relish Mills/Grinders: For finely chopped products like relish.
5. Brining/Fermentation (For Pickles):
Step: This is the heart of pickle making! Cucumbers are submerged in a salt brine solution within large tanks. Natural lactic acid bacteria ferment sugars, creating the characteristic tangy flavor and preserving the product.
Equipment:
Large Fermentation Tanks: Often made of fiberglass or food-grade plastic, holding thousands of gallons. They must be sealable.
Pumps & Piping: For transferring brine and cucumbers.
Brine Mixing Tanks: To prepare the salt solution accurately.
6. Desalting & Rinsing (For Fermented Pickles):
Step: After fermentation, excess salt is removed to achieve the desired final taste.
Equipment:
Tanks with flowing fresh water where pickles soak, or countercurrent washers that efficiently rinse salt away with progressively cleaner water.
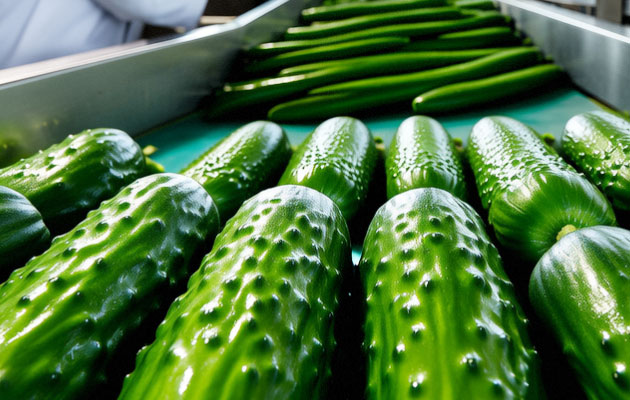

7. Final Inspection & Quality Control:
Step: Before packaging, another rigorous inspection ensures only top-quality product proceeds.
Equipment:
Final inspection belts under bright lights, often aided by more sophisticated automated vision systems and manual checkers. Samples are pulled for lab testing (pH, acidity, salt content, texture, flavor).
8. Filling & Packaging:
Step: The processed cucumbers (whole, sliced, spears, relish) are packed into their final containers with fresh brine, vinegar solution, or other packing liquids.
Equipment:
Automatic Fillers: Precisely measure and deposit cucumbers into jars, pouches, or bags.
Liquid Fillers: Add the packing solution (brine, vinegar, spices).
Cappers/Sealers: Apply lids to jars or seal bags/pouches.
Labelers: Apply product labels.
Case Packers: Place finished containers into shipping boxes.
9. Pasteurization (For Shelf-Stable Products):
Step: To ensure microbial safety and long shelf life without refrigeration, many products (especially jarred pickles) undergo heat treatment.
Equipment:
Continuous Pasteurizers/Tunnel Pasteurizers: Sealed jars/bags move through zones of progressively hotter water sprays or steam, then cooling zones. Time and temperature are tightly controlled.
10. Cooling, Drying & Storage:
Step: Pasteurized products are cooled to room temperature, dried to prevent label damage, then palletized for warehousing and distribution.
Equipment:Cooling tunnels, air knives/dryers, palletizers, and refrigerated or ambient warehouses.
Why it Matters:
This intricate process, guided by strict food safety standards , ensures the cucumbers we buy are safe, consistently high-quality, and delicious. Each piece of equipment plays a crucial role in maintaining that signature cucumber crunch – whether it ends up on your burger, in your salad, or straight from the jar! Next time you enjoy a pickle or a fresh cucumber slice, remember the fascinating journey it took through the cucumber processing plant.
If you want to set up a cucumber processing plant, you can contact us at any time. We are a manufacturer and exporter of cucumber processing equipment. We need cucumber washing machine, cucumber cutting machines, cucumber grading machines, etc. We can customize solutions according to your needs. You can contact us at any time: +8618595613260









 E_mail
E_mail contact
contact Whatsapp
Whatsapp TOP
TOP