Vegetable Processing Plant Project
Time:2024-12-20By:admin
The vegetable processing plant project is an initiative aimed at transforming fresh vegetables into a variety of products for consumption, preservation, and distribution. This blog will delve into the various aspects of setting up and managing a successful vegetable processing plant, from the initial planning stages to the day-to-day operations.
Market Analysis
Before embarking on the vegetable processing plant project, a thorough market analysis is crucial. This involves understanding the demand for processed vegetables, identifying target markets, and recognizing potential competitors. The analysis should also consider consumer preferences, which are increasingly leaning towards healthy and convenient food options.
Project Planning
1. Feasibility Study
The first step in the project planning phase is to conduct a feasibility study. This study will assess the economic viability of the project, including the cost of raw materials, processing equipment, labor, and potential profits.
2. Location Selection
The location of the plant is a critical factor. It should be close to the source of raw materials to minimize transportation costs and ensure the freshness of the vegetables. Additionally, proximity to major markets can facilitate distribution.
3. Equipment and Technology
Investing in the right equipment and technology is essential for efficiency and quality. This includes vegetable washing machine, vegetable slicers, vegetable drying machine, and vegetable packaging machinery. The choice of technology should align with the types of products to be processed, such as canned, frozen, or dehydrated vegetables.
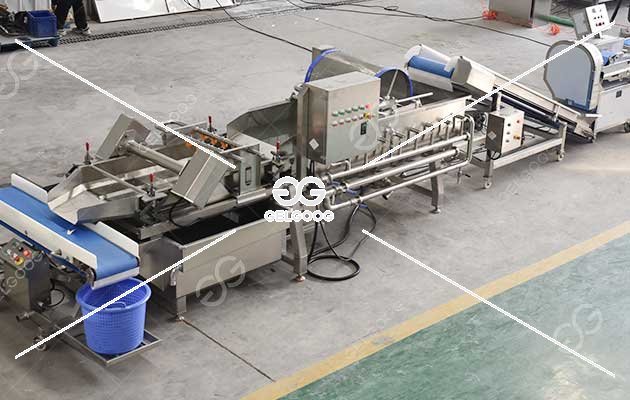


4. Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and complying with food safety regulations is non-negotiable. This includes obtaining necessary permits, adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and implementing Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems.
Production Process
The production process in a vegetable processing plant can be broken down into several stages:
1. Harvesting and Transportation
Fresh vegetables must be harvested at the peak of ripeness and transported to the plant with minimal delay to preserve their quality.
2. Cleaning and Sorting
Upon arrival, vegetables are thoroughly cleaned to remove dirt and debris. They are then sorted by size and quality to ensure uniformity in the final product.
3. Processing
This is where the vegetables are transformed into various products. Depending on the type of processing, this could involve cutting, cooking, canning, freezing, or dehydrating.
4. Packaging
Processed vegetables are packaged in a way that preserves their freshness and extends their shelf life. This could involve vacuum sealing, canning, or using modified atmosphere packaging.
5. Quality Control
Throughout the production process, quality control checks are performed to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.
Marketing and Distribution
Effective marketing is key to the success of any product. For a vegetable processing plant, this could involve:
Creating brand awareness through advertising and social media.
Establishing partnerships with retailers and food service providers.
Participating in trade shows and food expos to showcase products.
Distribution strategies should consider the perishability of the products and the need for efficient logistics to reach customers promptly.
Sustainability and Waste Management
A responsible vegetable processing plant project must incorporate sustainable practices. This includes reducing waste through efficient processing, recycling, and composting. Energy-efficient technologies and water conservation measures should also be considered.
Conclusion
The vegetable processing plant project is a venture that can contribute significantly to the food industry by providing consumers with a variety of high-quality, convenient, and nutritious vegetable products. By carefully planning, investing in the right technology, and adhering to best practices in production and marketing, a vegetable processing plant can be a profitable and sustainable business.









 E_mail
E_mail contact
contact Whatsapp
Whatsapp TOP
TOP